Science
Ancient Chewing Gum Reveals Gender Roles in Neolithic Europe
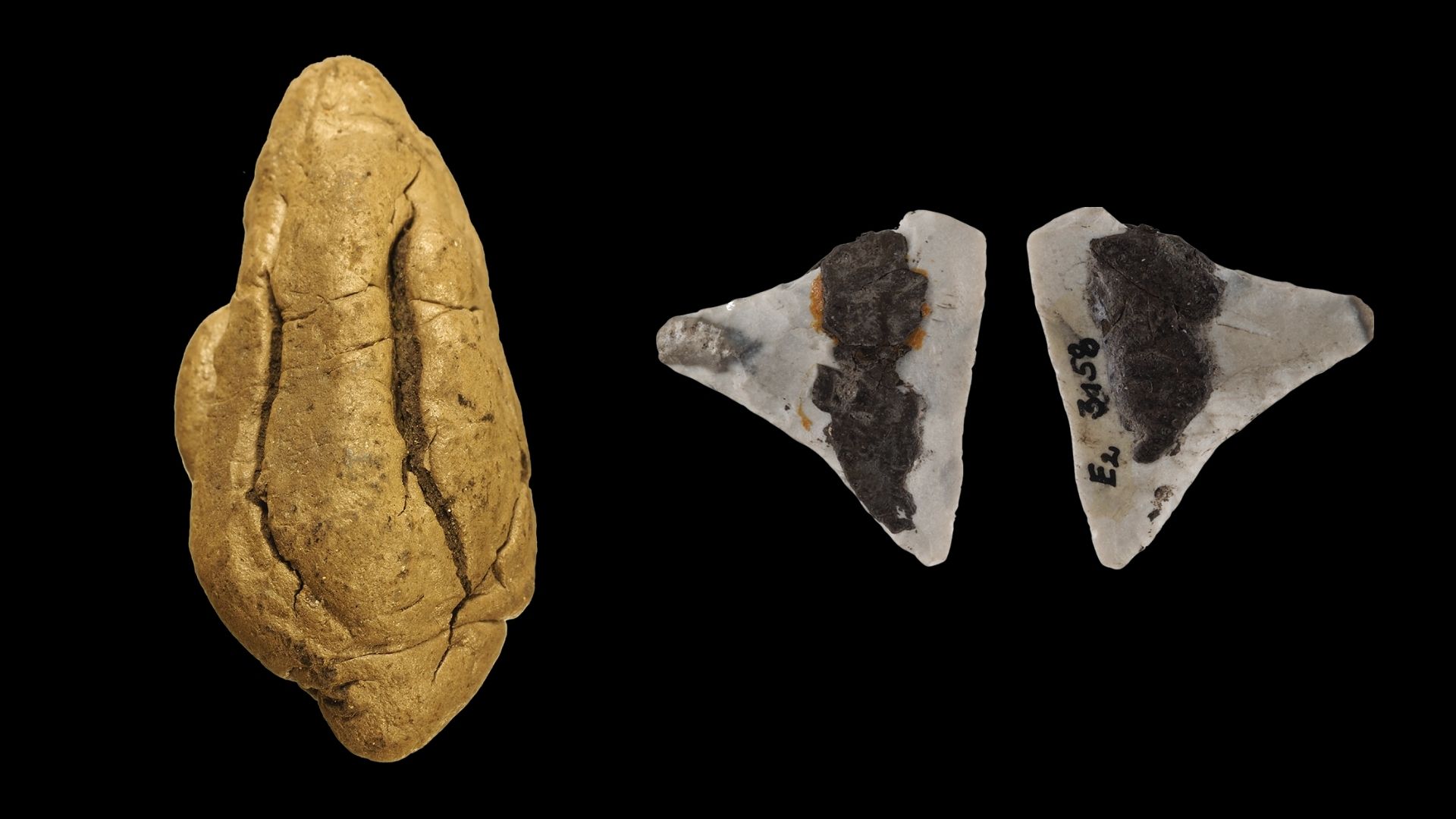
A recent study conducted by researchers from the University of Copenhagen has uncovered significant insights into gender roles during the Neolithic Age in Europe. By analyzing ancient birch tar artifacts, which were likely used as a form of “chewing gum” over 6,000 years ago, the researchers have provided a glimpse into daily life and the division of labor between men and women in early societies.
The research team examined 30 pieces of birch tar retrieved from nine archaeological sites in the European Alps, primarily from lake settlements. Among these artifacts, twelve tar pieces were identified as loose wads, indicating they had been chewed. The birch tar, known for its preservative qualities, contained traces of human saliva, food remnants, and even DNA, allowing the researchers to gain insights into the behaviors and practices of Neolithic communities.
According to the team, led by Anna White, the precise reasons for chewing birch tar remain uncertain. It is hypothesized that the substance may have been consumed for its medicinal properties, as it contains natural compounds with antimicrobial effects. The researchers noted, “The presence of human and oral microbial DNA in some of the samples suggests the tar was chewed, in some cases by multiple individuals.” This discovery enables a more nuanced understanding of gender dynamics in ancient societies.
Uncovering Gender Roles
The DNA analysis revealed intriguing patterns. Male DNA was predominantly found in tar used as an adhesive for ten stone tools, while female DNA was present in tar associated with three pottery items. This evidence led the researchers to conclude that men were primarily responsible for tool usage, whereas women engaged in pottery production during the Neolithic Age.
The study also suggested an alternative perspective on the use of chewing birch tar. The researchers proposed that Neolithic individuals may have chewed the tar to soften it for use as an adhesive, as it tends to harden upon cooling. They explained, “Saliva reduces adhesive properties, which can only be returned after reheating.” This finding may clarify why less oral microbial DNA was detected in the hafted samples and ceramic tars compared to the chewed pieces.
This research sheds light on a unique aspect of prehistoric life, providing a rare opportunity to explore gendered practices and dietary habits of ancient communities. As human remains from this period are scarce, the analysis of ancient chewing gum offers valuable insights that would otherwise be lost to time.
The findings from this study have been published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, contributing to our understanding of early human societies and the roles individuals played within them. By examining these ancient artifacts, researchers are not only uncovering the past but also enriching our knowledge of the complex social structures that existed thousands of years ago.
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoOhio State Study Uncovers Brain Connectivity and Function Links
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoHamas Chief Stresses Disarmament Tied to Occupation’s End
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Star π 1 Gruis
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoMegan Thee Stallion Exposes Alleged Online Attack by Bots
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Challenge 200-Year-Old Physics Principle with Atomic Engines
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoPaloma Elsesser Shines at LA Event with Iconic Slicked-Back Bun
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoFDA Unveils Plan to Cut Drug Prices and Boost Biosimilars
-

 Business2 months ago
Business2 months agoMotley Fool Wealth Management Reduces Medtronic Holdings by 14.7%
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoInnovator Captures Light at 2 Billion Frames Per Second
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoFederal Agents Detain Driver in Addison; Protests Erupt Immediately
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoBeloved Artist and Community Leader Gloria Rosencrants Passes Away









