Science
Scientists Investigate Unusual Behavior of Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS
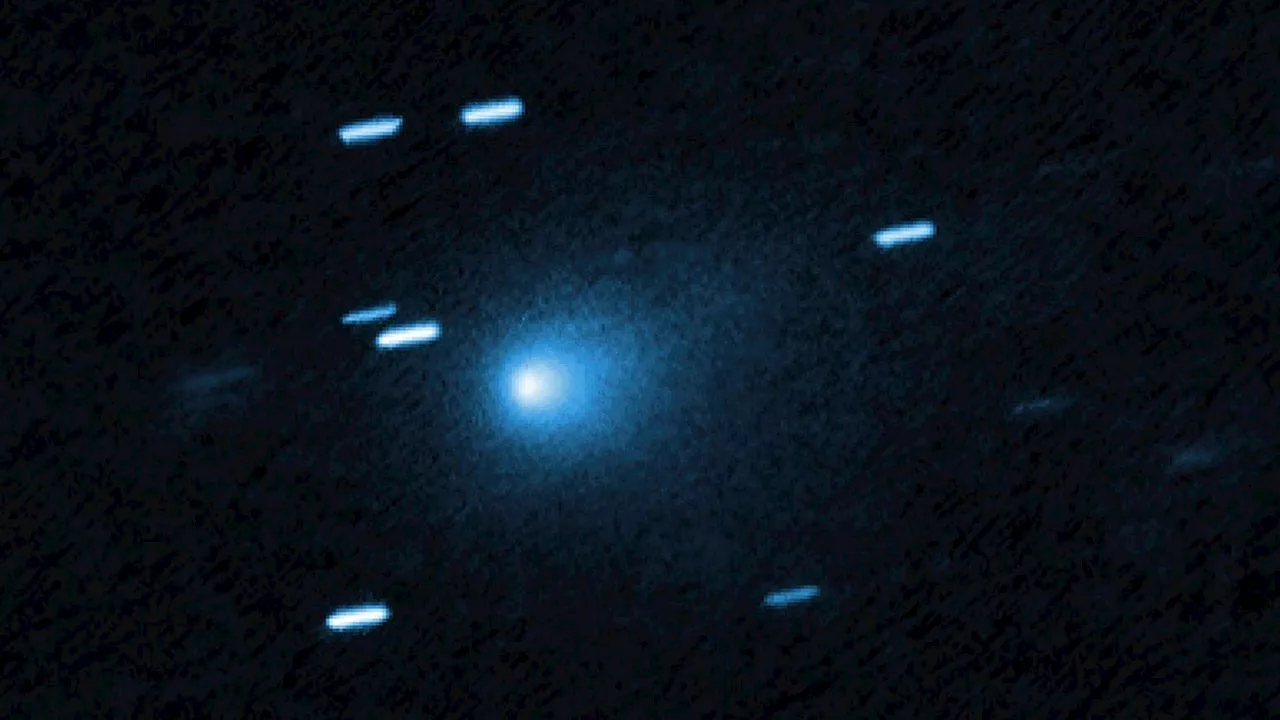

Scientists are investigating the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS, which has displayed unexpected characteristics following its closest approach to the sun. During its perihelion on October 29, 2023, 3I/ATLAS came within 203 million kilometers of the sun, exhibiting what Harvard theoretical physicist Dr. Avi Loeb describes as “non-gravitational acceleration.” The object also appeared to take on a bluer hue than the sun, a phenomenon that is atypical for comets. Furthermore, it lacks a cometary tail, which raises questions about its composition and origin.
The unusual behavior of 3I/ATLAS has prompted scientists to consider its potential connections to the enigmatic “Wow” signal, a radio signal detected in 1977. Dr. Loeb noted that both 3I/ATLAS and the Wow signal originated from similar directions in space, within nine degrees of each other. “The question is, were they related?” he remarked, emphasizing the need for further investigation into the object’s nature.
Monitoring 3I/ATLAS
As researchers continue to monitor 3I/ATLAS, some experts are cautious about jumping to conclusions regarding its origins. Dr. Ken Gayley, an astronomy professor at the University of Iowa, pointed out that while the object exhibits unusual behavior, it is essential to maintain an assumption of natural origins until compelling evidence suggests otherwise. “We would always start off with the assumption that these are natural objects,” he stated. “If there’s really very powerful evidence that they’re not, then we might be led toward another direction.”
3I/ATLAS is expected to be closest to Earth on December 19, 2023. Scientists are eager to gather more data during this period, which could provide insight into the formation and conditions of other star systems. Dr. Loeb expressed hope that the object would not present any unexpected dangers. “I hope we will not receive an unwanted gift for Christmas,” he quipped, referring to the potential risks of interstellar objects.
NASA has indicated that comets are typically named after their discoverers. In this instance, 3I/ATLAS is named after the team behind the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System survey telescope located in Rio Hurtado, Chile. The “I” in its name denotes that it is an interstellar object, marking it as the third known interstellar visitor, following 1I/Oumuamua in 2017 and 2I/Borisov in 2019.
Future Research and Implications
With scientists actively studying 3I/ATLAS, they are keen to ascertain its true nature and implications for our understanding of the universe. As researchers analyze the data collected from this object, they hope to unlock secrets that could reshape our knowledge of cosmic phenomena.
The investigation into 3I/ATLAS serves as a reminder of the mysteries that still exist beyond our solar system. As scientists continue their work, they remain committed to uncovering the truth behind this intriguing interstellar visitor.
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoHamas Chief Stresses Disarmament Tied to Occupation’s End
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoOhio State Study Uncovers Brain Connectivity and Function Links
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoMegan Thee Stallion Exposes Alleged Online Attack by Bots
-

 Science3 weeks ago
Science3 weeks agoResearchers Challenge 200-Year-Old Physics Principle with Atomic Engines
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoFederal Agents Detain Driver in Addison; Protests Erupt Immediately
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoPaloma Elsesser Shines at LA Event with Iconic Slicked-Back Bun
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoHome Depot Slashes Prices on Halloween Favorites Up to 75%
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoOrioles Hire Craig Albernaz as New Manager Amid Rebuild
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoSyracuse Stage Delivers Lively Adaptation of ‘The 39 Steps’
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoWill Smith Powers Dodgers to World Series Tie with Key Homer
-

 World3 weeks ago
World3 weeks agoGlobal Military Spending: Air Forces Ranked by Budget and Capability
-

 Politics3 weeks ago
Politics3 weeks agoNHP Foundation Secures Land for 158 Affordable Apartments in Denver