Health
New Enzyme Shows Promise in Combatting Autoimmune Diseases
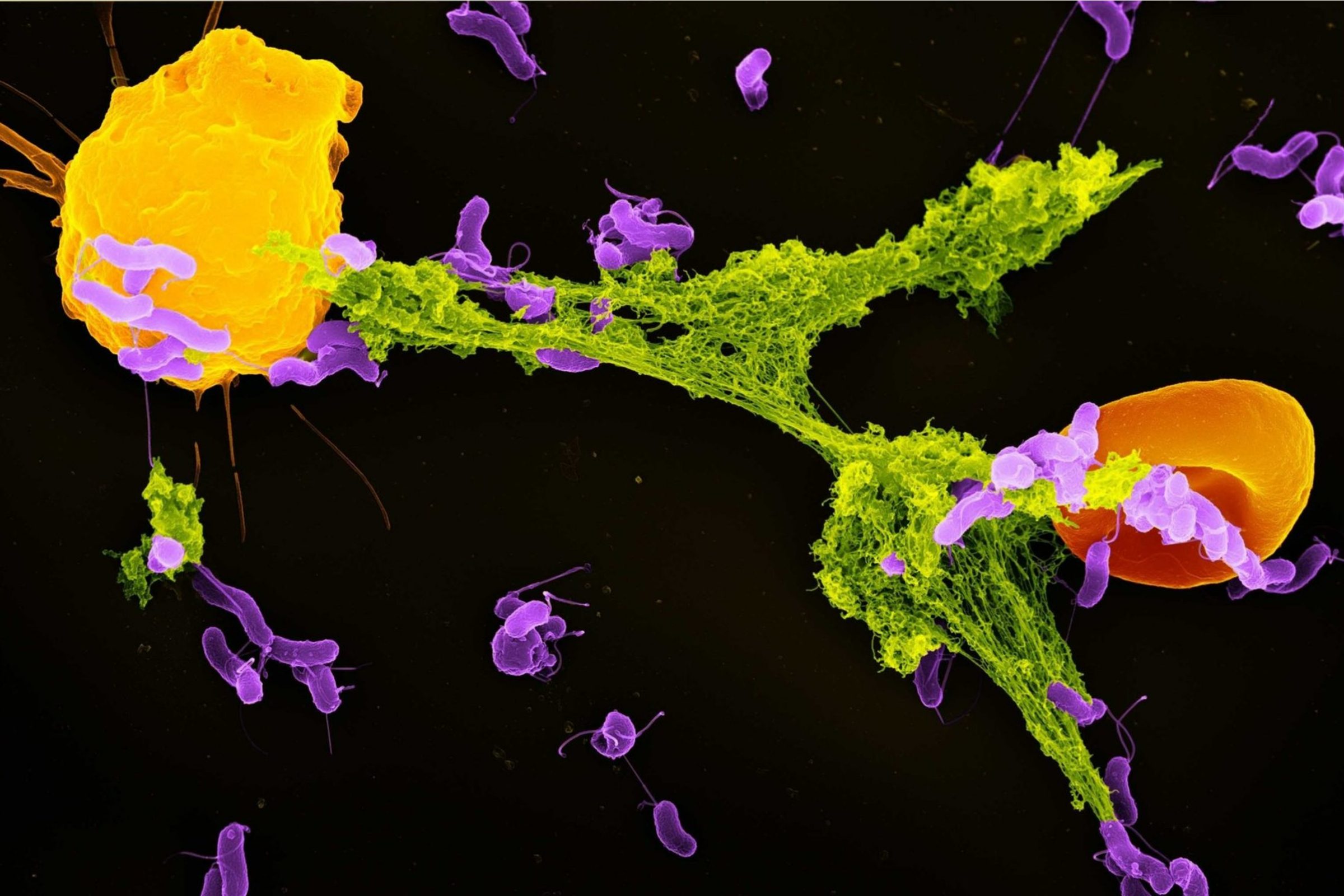
A recently developed DNA-chopping enzyme has shown potential in breaking down neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), offering a novel approach to fighting autoimmune diseases. Preliminary data from research conducted by Neutrolis suggests that this enzyme could play a significant role in altering the management of such conditions.
Neutrophils, a type of white blood cell, are key components of the immune system. In their defense against pathogens, these cells expel strands of DNA that form NETs, which ensnare and kill bacteria. While this response is crucial for fighting infections, the excessive formation of NETs has been linked to various autoimmune diseases, including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
The research highlights that by using this new enzyme, it may be possible to dismantle the NETs, thereby reducing their potentially harmful effects in autoimmune responses. This innovative approach aims to shift the focus from merely suppressing the immune system, which is the current standard treatment, to addressing the underlying mechanisms that contribute to autoimmune disorders.
Clinical trials are currently in the planning stages, with the first set of data expected to be published in early 2024. Researchers emphasize the importance of these findings, as they could provide a new pathway for patients suffering from these chronic conditions. The potential for this enzyme to target and break down NETs may lead to a more effective treatment strategy that minimizes side effects associated with traditional therapies.
Experts in the field are optimistic about the implications of this research. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading immunologist at the University of London, remarked, “If these early findings are confirmed in subsequent studies, we could see a significant shift in how autoimmune diseases are treated.” The focus on NETs could pave the way for targeted therapies that improve patient outcomes.
As the research progresses, the scientific community is eager to further explore the enzyme’s mechanisms and applications. If successful, this could represent a breakthrough not only in the understanding of autoimmune diseases but also in the broader context of immune system functioning.
Overall, the findings from Neutrolis underscore the ongoing quest for more effective treatments for autoimmune diseases. With the potential to transform patient care, this research may open new avenues for therapeutic interventions and enhance the quality of life for those affected.
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoResearchers Challenge 200-Year-Old Physics Principle with Atomic Engines
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoNHP Foundation Secures Land for 158 Affordable Apartments in Denver
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoBoeing’s Aircraft Production: Assessing Numbers and Challenges
-

 Entertainment4 days ago
Entertainment4 days agoSyracuse Stage Delivers Lively Adaptation of ‘The 39 Steps’
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoLongtime Friends Face Heartbreak After Loss and Isolation
-

 Science4 days ago
Science4 days agoAI Misidentifies Doritos Bag as Gun, Triggers Police Response
-

 Lifestyle4 days ago
Lifestyle4 days agoRed Bluff High School’s Elli Nolan Named Rotary Student of the Month
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoNeuroscientist Advocates for Flag Football Until Age 14
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoSpirit Airlines Cuts Workforce with Furloughs for 365 Pilots
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoGlobal Military Spending: Air Forces Ranked by Budget and Capability
-

 Lifestyle3 days ago
Lifestyle3 days agoTrump’s Push to Censor National Parks Faces Growing Backlash
-

 Top Stories5 days ago
Top Stories5 days agoUrgent Search for Suspect Who Exposed Himself to Teen Girl