Health
Harvard Study Unveils Key Metabolites in Obesity and Diabetes Control
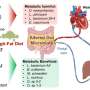
Research from Harvard University has revealed a significant connection between intestinal metabolites and the regulation of obesity and type 2 diabetes. As detailed in a recent publication in the journal Cell Metabolism, these metabolites originate in the intestine, travel to the liver, and eventually reach the heart, where they circulate throughout the body.
The study highlights how these metabolites are crucial in managing metabolic pathways within the liver and influencing insulin sensitivity. Understanding this mechanism may pave the way for novel treatment strategies targeting obesity and type 2 diabetes, two conditions that affect millions globally.
Insights into Metabolite Functionality
The research team identified a specific group of metabolites that play a vital role in metabolic processes. By tracing the journey of these compounds from the intestine to the liver and heart, scientists uncovered their influence on how the body responds to insulin. Enhanced insulin sensitivity is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and preventing the onset of diabetes.
The findings suggest that these metabolites could be potential biomarkers for assessing metabolic health. Moreover, they open avenues for developing therapies that could mitigate the effects of obesity and type 2 diabetes. This is particularly relevant given the rising prevalence of these metabolic disorders, which have become a significant public health concern worldwide.
Implications for Future Research and Treatment
The implications of this study extend beyond academic curiosity. With obesity and type 2 diabetes on the rise, understanding the underlying mechanisms is critical for devising effective interventions. The metabolites identified in the research may serve as targets for future drugs aimed at improving metabolic health.
As the scientific community continues to explore the intricate relationships between diet, metabolism, and health, this study exemplifies the importance of interdisciplinary research. By combining insights from biochemistry, nutrition, and physiology, researchers can develop a more comprehensive understanding of how to combat these complex health issues.
In conclusion, the work conducted at Harvard University sheds light on the significant role intestinal metabolites play in the regulation of obesity and type 2 diabetes. As research progresses, it could lead to groundbreaking treatments that improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoOhio State Study Uncovers Brain Connectivity and Function Links
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoHamas Chief Stresses Disarmament Tied to Occupation’s End
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoMegan Thee Stallion Exposes Alleged Online Attack by Bots
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project for Disaster Monitoring
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoResearchers Challenge 200-Year-Old Physics Principle with Atomic Engines
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoPaloma Elsesser Shines at LA Event with Iconic Slicked-Back Bun
-

 World1 month ago
World1 month agoFDA Unveils Plan to Cut Drug Prices and Boost Biosimilars
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoFederal Agents Detain Driver in Addison; Protests Erupt Immediately
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoBeloved Artist and Community Leader Gloria Rosencrants Passes Away
-

 Business1 month ago
Business1 month agoMotley Fool Wealth Management Reduces Medtronic Holdings by 14.7%
-

 Politics1 month ago
Politics1 month agoNHP Foundation Secures Land for 158 Affordable Apartments in Denver
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoALMA Discovers Companion Orbiting Giant Star π 1 Gruis








