Health
Excessive Screen Time: Understanding Its Impact on Health
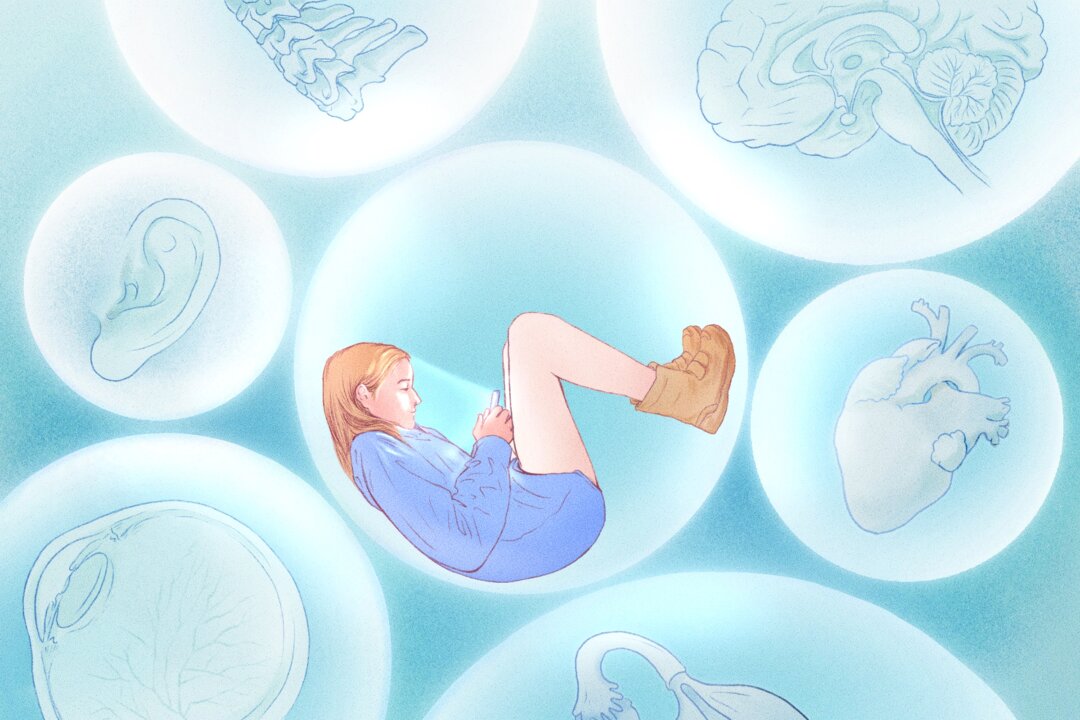
The rise of smartphones has transformed daily routines, with the average American adult reaching for their device approximately 144 times a day. This shift has resulted in increased screen time, which growing research indicates can negatively affect various organs in the body. From the eyes to the heart and spine, the consequences of prolonged exposure to screens are becoming clearer as experts study the long-term impacts of digital device usage.
Research highlights that the blue light emitted by screens can lead to eye strain and discomfort, often referred to as digital eye strain or Computer Vision Syndrome. Symptoms include dryness, irritation, and blurred vision. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), blue light exposure, particularly in the evening, can disrupt sleep patterns by interfering with the body’s natural circadian rhythms.
Effects on Major Organ Systems
Excessive screen time is not limited to visual issues; it also extends to cardiovascular health. Studies suggest that prolonged sitting while using a smartphone or computer may contribute to a sedentary lifestyle, which is associated with an increased risk of heart disease. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) advises that maintaining a balance between screen time and physical activity is essential for overall health.
Additionally, the sedentary posture adopted during screen use can affect spinal health. Prolonged sitting, particularly in poor posture, can lead to back and neck pain, which many adults report as a growing concern. Experts recommend regular breaks and ergonomic adjustments to reduce strain on the spine and surrounding muscles.
Emerging research also points to potential links between screen time and mental health issues, particularly among younger populations. High levels of screen engagement have been associated with increased rates of anxiety and depression in adolescents. The constant exposure to social media can lead to feelings of inadequacy and low self-esteem, as users often compare their lives to curated representations of others.
Mitigating the Impact
To combat the negative effects of screen time, health professionals recommend several strategies. The AAP suggests implementing the “20-20-20 rule,” where individuals take a 20-second break to look at something 20 feet away every 20 minutes of screen use. This practice can help alleviate eye strain and promote healthier viewing habits.
Moreover, limiting screen time, especially before bedtime, is crucial for improving sleep quality. Reducing exposure to screens at least an hour before sleep can help the body produce melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep cycles.
As society becomes increasingly reliant on digital devices, it is essential to recognize and address the potential health risks associated with excessive screen time. By adopting healthier habits and being mindful of usage patterns, individuals can protect their physical and mental well-being in this digital age.
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoResearchers Challenge 200-Year-Old Physics Principle with Atomic Engines
-

 Entertainment1 week ago
Entertainment1 week agoSyracuse Stage Delivers Lively Adaptation of ‘The 39 Steps’
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoGlobal Military Spending: Air Forces Ranked by Budget and Capability
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoNHP Foundation Secures Land for 158 Affordable Apartments in Denver
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoNFL Confirms Star-Studded Halftime Show for Super Bowl LVIII
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoBoeing’s Aircraft Production: Assessing Numbers and Challenges
-

 Lifestyle7 days ago
Lifestyle7 days agoTrump’s Push to Censor National Parks Faces Growing Backlash
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoRed Bluff High School’s Elli Nolan Named Rotary Student of the Month
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoNeuroscientist Advocates for Flag Football Until Age 14
-

 Top Stories1 week ago
Top Stories1 week agoUrgent Search for Suspect Who Exposed Himself to Teen Girl
-

 Health2 weeks ago
Health2 weeks agoFDA Launches Fast-Track Review for Nine Innovative Therapies
-

 Lifestyle2 weeks ago
Lifestyle2 weeks agoLongtime Friends Face Heartbreak After Loss and Isolation