Health
New RNA Molecule Offers Hope Against Neurodegenerative Diseases
Recent research has unveiled a novel RNA molecule, identified as FAM151B-DT, that may play a crucial role in preventing the aggregation of proteins linked to neurodegenerative diseases. These conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and frontotemporal lobar dementia (FTLD-tau), are characterized by the progressive loss of neurons and cognitive decline. The findings, published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, indicate that FAM151B-DT could serve as an essential regulator of protein homeostasis in the brain.
Research teams from Washington University in St. Louis and the University of California conducted an extensive investigation into the functions of this newly discovered RNA molecule. Previous studies have established a connection between neurodegenerative diseases and the accumulation of misfolded proteins, including tau and α-synuclein. These proteins, while necessary for normal brain function, can become harmful when they aggregate abnormally.
The research team, led by Arun Renganathan and Miguel A. Minaya, utilized transcriptomics, mass spectrometry, and biochemical assays to clarify the role of FAM151B-DT in tau pathophysiology. They noted, “Neurodegenerative diseases share common features of protein aggregation along with other pleiotropic traits, including shifts in transcriptional patterns, neuroinflammation, disruption in synaptic signaling, mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and impaired clearance mechanisms like autophagy.” The study aimed to identify key regulators of these interconnected traits.
Examining Protein Aggregation and RNA’s Role
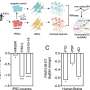
In their research, Renganathan and colleagues analyzed stem cells and brain tissue samples from individuals diagnosed with neurodegenerative diseases. They discovered that the levels of FAM151B-DT were notably reduced in samples from patients with FTLD-tau, progressive supranuclear palsy, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease. The researchers concluded that silencing FAM151B-DT in vitro led to increased aggregation of tau and α-synuclein proteins, exacerbating the conditions associated with these diseases.
The study employed stem cells grown in laboratory settings, where researchers silenced the identified RNA molecule. This manipulation resulted in heightened protein aggregation, suggesting that FAM151B-DT functions as a protective agent against the accumulation of detrimental proteins. “To begin to understand the mechanism by which FAM151B-DT mediates tau aggregation and contributes to several neurodegenerative diseases, we deeply characterized this novel lncRNA and found that FAM151B-DT resides in the cytoplasm where it interacts with tau, α-synuclein, HSC70, and other proteins involved in protein homeostasis,” the authors stated.
Implications for Future Treatments
The implications of this study are significant. The findings indicate that enhancing the expression of FAM151B-DT may facilitate the autophagic clearance of phosphorylated tau and α-synuclein, thereby reducing their aggregation. This suggests that FAM151B-DT could offer a new avenue for therapeutic intervention in neurodegenerative diseases.
The research concludes that targeting FAM151B-DT may provide a promising strategy for early treatment or symptom management in patients suffering from these debilitating conditions. The authors emphasize, “Overall, these findings pave the way for further exploration of FAM151B-DT as a promising molecular target for several neurodegenerative diseases.”
As understanding of the mechanisms behind neurodegenerative diseases continues to evolve, research like this underscores the potential of novel RNA molecules in addressing the challenges posed by these complex conditions. The hope is that further investigation into FAM151B-DT could lead to breakthroughs in treatment options for millions affected worldwide.
-

 Politics2 weeks ago
Politics2 weeks agoHamas Chief Stresses Disarmament Tied to Occupation’s End
-

 Science2 weeks ago
Science2 weeks agoOhio State Study Uncovers Brain Connectivity and Function Links
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoMegan Thee Stallion Exposes Alleged Online Attack by Bots
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoResearchers Challenge 200-Year-Old Physics Principle with Atomic Engines
-

 Entertainment2 weeks ago
Entertainment2 weeks agoPaloma Elsesser Shines at LA Event with Iconic Slicked-Back Bun
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoFederal Agents Detain Driver in Addison; Protests Erupt Immediately
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoMotley Fool Wealth Management Reduces Medtronic Holdings by 14.7%
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoHome Depot Slashes Prices on Halloween Favorites Up to 75%
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoOrioles Hire Craig Albernaz as New Manager Amid Rebuild
-

 World2 weeks ago
World2 weeks agoFDA Unveils Plan to Cut Drug Prices and Boost Biosimilars
-

 Entertainment3 weeks ago
Entertainment3 weeks agoSyracuse Stage Delivers Lively Adaptation of ‘The 39 Steps’
-

 Top Stories2 weeks ago
Top Stories2 weeks agoWill Smith Powers Dodgers to World Series Tie with Key Homer